Table of Contents
The Ladakh map of India shows the location of the Union Territory of Ladakh, which is situated in the Himalayas between the Kashmir Valley and Tibet. It is in the northernmost region of India and has a rich historical legacy as it was a part of the Silk Route.
Ladakh is one of the oldest surviving civilizations in India with numerous archaeological sites spread all over its landscape. The Kargil War, fought between India and Pakistan in 1999 was primarily fought for the control of this region.
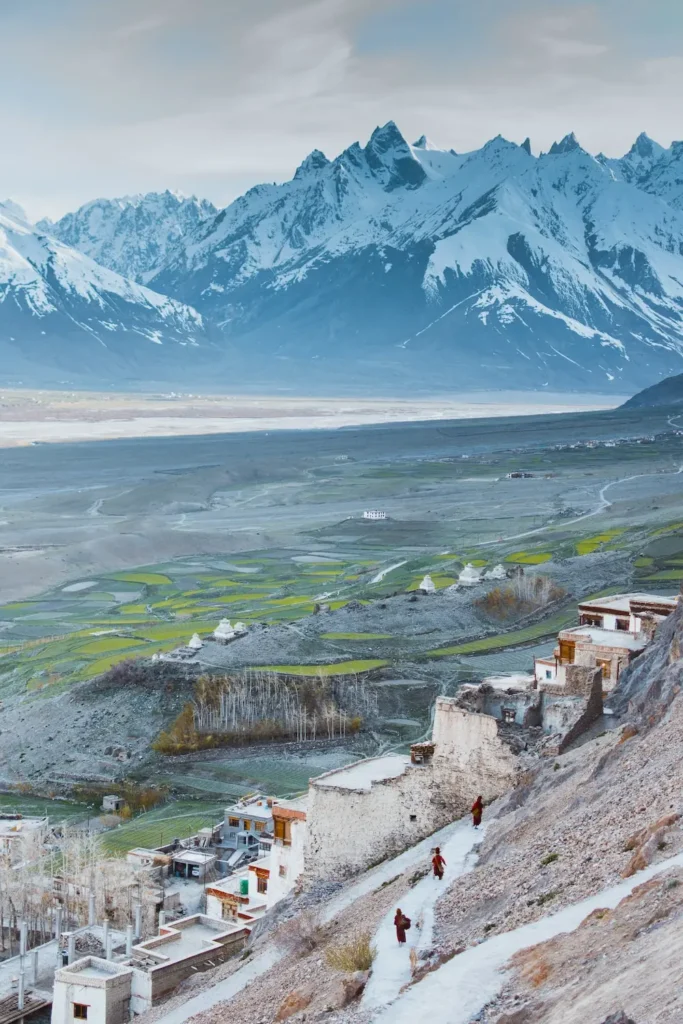

Ladakh is a beautiful region with a unique blend of Buddhist and Tibetan cultures, characterized by high-altitude deserts and stunning mountain ranges. There are ancient monasteries to explore and exciting outdoor activities like trekking and mountaineering to enjoy.
This blog post aims to give readers an in-depth understanding of Ladakh’s position on the map of India, its historical context, recent political changes, and its significance to India.
We will talk about the best places to visit in Ladakh. We will also give information that will help people when they travel there. After reading this, you will know more about Ladakh’s culture, how beautiful it is, and why it is important for India.
Ladakh Map of India and Its Location
Located in the north of India, Ladakh shares borders with Tibet to the east, Pakistan to the west, and the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir to the south. The region covers an area of about 59,146 square kilometres and is divided into two districts, Leh and Kargil.
Looking at a detailed map can help you locate Ladakh on India’s map. Ladakh is situated in the northernmost part of India, above Himachal Pradesh state, and east of Jammu and Kashmir. It’s a high-altitude desert region, crossed by mountain ranges such as the Karakoram and the Himalayas.
Ladakh’s geography is unique, with barren hills and valleys, high-altitude deserts, and glacial lakes. The region is situated at an altitude ranging from 9,000 to 25,000 feet above sea level and is known for its extreme climatic conditions. In the winter months, temperatures can drop as low as -30 degrees Celsius, and in the summer, temperatures can reach up to 25 degrees Celsius.
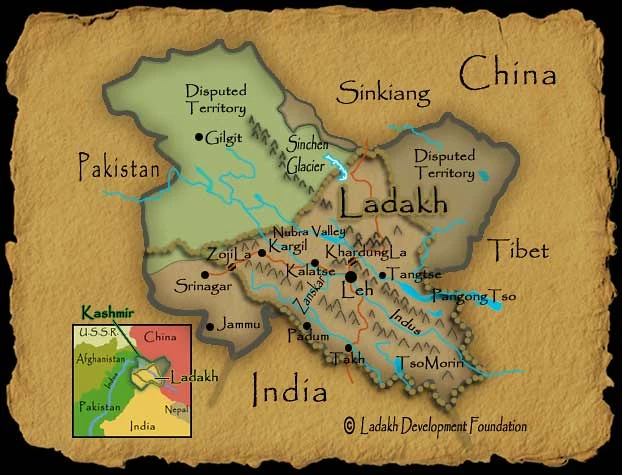
The topography of Ladakh is dominated by two mountain ranges: the Karakoram and the Himalayas. The Karakoram Range lies to the north and northeast of Ladakh and is home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including K2 and Gasherbrum. The Himalayas lie to the south of Ladakh, and the Zanskar Range lies to the west. Ladakh is also known for its high-altitude lakes, such as Pangong Tso and Tso Moriri, which are popular tourist attractions.
Historical Background of Ladakh Map of India
The union territory of Ladakh has a rich historical significance and a diverse cultural heritage that has been shaped by its location on the ancient Silk Route, its proximity to Tibet, and the influence of Buddhism.
Ladakh’s earliest known history dates back to the 2nd century BC when it was part of the Kushan Empire. Over time, it came under the control of various rulers, including the Tibetan Empire, the Kashmiri Kingdom, and the Mughal Empire.
In the 17th century, Ladakh was ruled by the Namgyal dynasty, which played a significant role in shaping the region’s cultural heritage. The Namgyal rulers were strong patrons of Buddhism, and they built many monasteries and stupas across the region. The Hemis Monastery, which is the largest and wealthiest monastery in Ladakh, was built during this period.
In the 19th century, Ladakh became a part of the Sikh Empire, and later it came under the control of the Dogra rulers of Jammu and Kashmir. The Dogra rulers were instrumental in building infrastructure in Ladakh, including roads and bridges, which helped to open up the region to trade and commerce.
In the 20th century, Ladakh saw significant political upheaval. It was a part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir when India gained independence from the British in 1947. However, in 1948, Pakistan invaded Jammu and Kashmir, and a war broke out between India and Pakistan. As a result, Ladakh became strategically important for India.
In 1971, Ladakh was given the status of a union territory within the Indian Republic, and it has been an integral part of India ever since. Today, Ladakh is a melting pot of cultures, with influences from Tibet, Central Asia, and India. Its rich history and cultural heritage have made it a popular destination for tourists who come to explore its ancient monasteries, traditional festivals, and stunning landscapes.
Recent Political Developments in Ladakh Map of India
The union territory of Ladakh has seen significant political developments in recent years, especially since the Indian government revoked Article 370 of the Indian Constitution in 2019. Article 370 granted a special autonomous status to the state of Jammu and Kashmir, which included Ladakh.
After the revocation of Article 370, the Indian government bifurcated the state of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories: Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. Ladakh was given the status of a union territory without a legislature, which means that it is now governed directly by the central government in New Delhi.
The decision to create Ladakh as a separate union territory was seen as a significant development for the region, as it will allow for more direct control over local governance and development. The move was welcomed by many Ladakhi leaders and residents who had long been demanding greater autonomy and control over their region’s affairs.
However, the decision was not without controversy. Some critics have argued that the move could lead to further marginalization of Ladakh’s Muslim population, who had benefited from the special status granted to the former state of Jammu and Kashmir. Others have expressed concern that the decision could lead to further conflict between India and Pakistan, as the disputed territory of Jammu and Kashmir remains a contentious issue between the two countries.
Overall, the revocation of Article 370 and the creation of The union territory of Ladakh represents a significant shift in the political landscape of the region. The move has both positive and negative implications for Ladakh’s future, and it remains to be seen how it will affect the region’s development and relationship with the central government in New Delhi.
Districts of Ladakh and New Proposed Districts
Ladakh is currently divided into two districts: Leh and Kargil. Leh district covers the eastern part of Ladakh, while Kargil district covers the western part. However, there have been recent proposals to create new districts within Ladakh to improve governance and administrative efficiency.
The Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LAHDC) has proposed the creation of two new districts: Zanskar and Drass. Zanskar would be carved out of the Kargil district and Drass out of the current Kargil and Leh districts. These proposals are currently being considered by the Indian government.
Zanskar is a remote and mountainous region located in the western part of Ladakh. It is home to several Buddhist monasteries and is known for its scenic beauty. Creating a separate district would allow for better administration and development of this region.
Drass is located in the northern part of Kargil district and is known for its high-altitude terrain and harsh climate. It is the second coldest inhabited place in the world and experiences heavy snowfall in winter. Creating a separate district would help in the development of this region, which is currently neglected due to its remote location and harsh climate.
Importance of Ladakh for India
The union territory of Ladakh is a strategically important region for India due to its location on the border with China and Pakistan. The region is situated at a high altitude and is home to several key mountain passes, including the Khardung La and the Chang La, which are vital for India’s military presence in the region.
Ladakh’s strategic location also plays a significant role in India’s foreign policy. India has had a long-standing territorial dispute with China over the region of Aksai Chin, which is currently under Chinese control but is claimed by India as part of Ladakh. This dispute has led to several standoffs between Indian and Chinese troops in the region, including a tense standoff in 2020 that lasted for several months.
The Ladakh region is also important for India’s relationship with Pakistan. The Line of Control (LoC) between India and Pakistan runs through Ladakh, and the region has been the site of several skirmishes between Indian and Pakistani troops over the years.
In addition to its geopolitical significance, Ladakh is also an important region for India’s internal security. The region has a diverse population, including Buddhists, Muslims, and Hindus, and has seen occasional outbreaks of sectarian violence. India has also been concerned about the potential for infiltration by militants from Pakistan.
Overall, Ladakh’s strategic location and complex security situation make it a critical region for India’s internal and external security. The ongoing geopolitical tensions in the region, particularly with China, will continue to shape India’s foreign policy and military strategy in the years to come.
Tourist Attractions in Ladakh
Ladakh is a popular tourist destination in India, known for its stunning landscapes, rich culture, and unique way of life. Here are some of the top tourist attractions in Ladakh:
- Pangong Tso Lake: This picturesque lake is situated at a height of over 14,000 feet and stretches over 134 km from India to China. The crystal-clear waters of the lake change colour throughout the day, making it a popular destination for photographers and nature lovers.
- Nubra Valley: Located in the northeast of Ladakh, the Nubra Valley is known for its stark beauty, sand dunes, and ancient monasteries. Visitors can ride on Bactrian camels, also known as double-humped camels, and explore the valley’s unique landscape.
- Leh Palace: This nine-story palace was built in the 17th century by the ruler of Ladakh and served as the royal residence until the mid-19th century. Visitors can explore the palace’s architecture, artwork, and artefacts that offer a glimpse into Ladakh’s rich history.
- Hemis National Park: Spread over 4,400 square kilometres, Hemis National Park is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including the snow leopard, Himalayan black bear, and golden eagle. The park also features several Buddhist monasteries, including the Hemis Monastery, which is one of the largest and oldest in Ladakh.
- Shanti Stupa: Located on a hilltop overlooking Leh, the Shanti Stupa is a white-domed Buddhist monument built to promote world peace. Visitors can climb the steps to the top of the stupa and enjoy panoramic views of the surrounding mountains and valleys.
- Magnetic Hill: This natural wonder is located on the Leh-Kargil-Baltic highway and is known for its magnetic properties that appear to pull cars uphill. Visitors can experience the magnetic illusion and explore the surrounding area’s unique geological features.
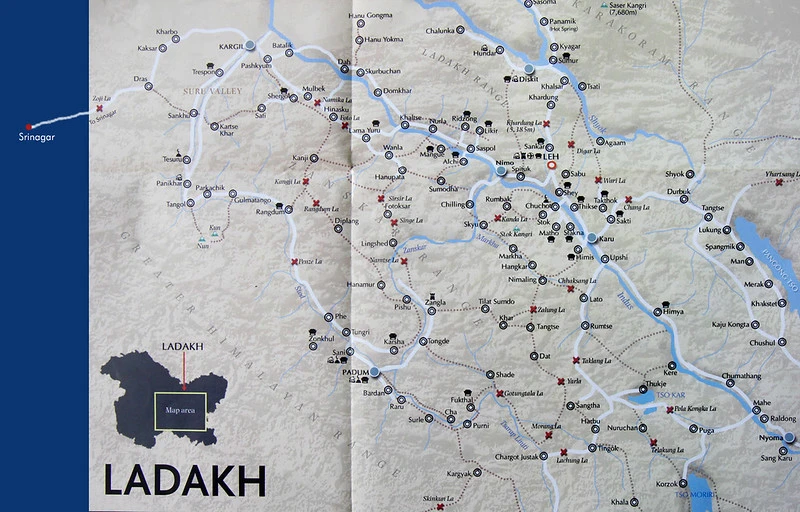
List of Most Visited Places To Visit From the Map of Ladakh
| Place | Altitude (meters) | Distance from Leh (km) | Travel Time (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pangong Tso Lake | 4,350 | 160 | 4-5 |
| Nubra Valley | 3,048 | 150 | 4-5 |
| Khardung La Pass | 5,359 | 40 | 1.5-2 |
| Magnetic Hill | 4,100 | 30 | 1 |
| Tso Moriri Lake | 4,522 | 220 | 6-7 |
| Hemis National Park | 3,500 | 40 | 1-2 |
| Leh Palace | 3,200 | 2 | 10-15 minutes |
| Shanti Stupa | 4,267 | 5 | 20-30 minutes |
| Spituk Monastery | 3,307 | 8 | 30-40 minutes |
| Alchi Monastery | 3,100 | 70 | 2-3 |
| Turtuk | 3,000 | 205 | 6-7 |
| Siachen Basecamp | 5,400 | 270 | 10-12 |
| Hanle | 4,200 | 255 | 7-8 |
| Panamik | 3,800 | 120 | 4-5 |
| Kargil | 2,676 | 210 | 6-7 |
Travel Information for Visitors to Ladakh Map of India
If you are planning a trip to Ladakh, here is some essential travel information you should know:
- How to Get There: The easiest way to reach Ladakh is by air, with flights available from major Indian cities like Delhi, and Mumbai. Alternatively, visitors can travel by road from Srinagar or Manali, although the journey can be challenging due to high altitudes and rough terrain.
- Best Time to Visit: The best time to visit Ladakh is between May and September when the weather is mild and the roads are open. However, visitors should be aware that Ladakh is a high-altitude desert and temperatures can drop sharply at night, even in summer.
- Visa Requirements: Visitors to Ladakh must have a valid Indian visa, which can be obtained from the Indian embassy or consulate in their home country. Some nationalities may also be eligible for an e-visa, which can be applied online.
- Safety Precautions: Ladakh is a remote and rugged region, and visitors should take precautions to ensure their safety. This includes staying hydrated, avoiding excessive physical activity, and acclimatizing to the high altitude before embarking on any strenuous activities. Visitors should also be aware of the risk of sunburn and wear protective clothing and sunscreen.
- Permits: Visitors to some areas of Ladakh, such as Pangong Tso Lake and Nubra Valley, require a permit to enter. These permits can be obtained from the local authorities in Leh or from authorized travel agencies.
Conclusion
Ladakh is a stunning and remote region of India, with breathtaking landscapes and unique culture. From crystal-clear lakes to ancient monasteries, there are many sights to explore in Ladakh. However, visitors should take precautions to ensure their safety by staying hydrated and wearing protective clothing. Additionally, permits are required for some areas of Ladakh and can be obtained from either the local authorities or authorized travel agencies. With proper planning and preparation, visitors can enjoy a safe and unforgettable trip to this magical region.
FAQ
Q: Which state is Ladakh in India?
A: The union territory of Ladakh is located in the northern part of India. It was earlier in the Jammu and Kashmir state.
Q: Where is Ladakh situated in India map?
A: Ladakh is a union territory located in the northern part of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the Great Himalayas to the south. It borders China on the east and Pakistan on the west.
Q: In which city is Ladakh?
A: The capital city of Ladakh is Leh. It is located at an altitude of 3,500 meters and is one of the highest cities in India.
Q: Which is capital of Ladakh?
A: The capital of Ladakh is Leh. It is located at an altitude of 3,500 meters and is one of the highest cities in India.
Q: In which state is Ladakh?
A: Ladakh is a union territory located in the northern part of India, formerly part of Jammu and Kashmir state. It borders China on the east and Pakistan on the west.
Q: Is Ladakh located in Jammu and Kashmir?
A: Ladakh was previously part of the Jammu and Kashmir state, but it is now a separate union territory since August 2019.
Q: Why is Ladakh famous?
A: Ladakh is famous for its beautiful landscapes, unique culture, and ancient monasteries. It also offers breathtaking views of the Himalayas, crystal-clear lakes, and stunning deserts. Visitors can enjoy a range of outdoor activities such as trekking, mountaineering, and camping.
It is also known for having some of the highest roads in the world.
It is a popular destination for adventure seekers, offbeat travellers and spiritual monks alike.
Q: Where is Ladakh located in which state?
A: Ladakh is a union territory located in the northern part of India. It borders China on the east and Pakistan on the west and formerly was part of Jammu and Kashmir state.
Q: How many countries touch Ladakh?
A: Ladakh shares borders with two countries, China to the east and Pakistan to the west. It does not share a border with any other country.
Q: Is Ladakh in India or Tibet?
A: Ladakh is located in India. It was previously part of the Jammu and Kashmir state, but it is now a separate union territory since August 2019.
Q: What is the 4 capital of Ladakh?
A: The capital of Ladakh is Leh. It is located at an altitude of 3,500 meters and is one of the highest cities in India. Additionally, there are three other major towns in Ladakh: Kargil, Dras and Nubra Valley. Each town has its own unique culture and identity. New areas are being proposed as districts like Zanskar, Changthang, Khaltsi and Turtuk.
Q: Where is the Ladakh in the Indian map?
A: Ladakh is a union territory located in the northern part of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the Great Himalayas to the south. It borders China on the east and Pakistan on the west and can be seen on an Indian map by looking for its border with those two countries.
If you are looking for unique accommodation for a stay in Leh, then look no further and explore one of the best camp resorts in Leh.


Leave a Reply